Ginger is one of the most loved spices in Indian homes. From smoothing a sore throat to helping digestion after a heavy meal, it is part of daily life in teas, curries and chutneys. Packed with nutrients and healing properties, ginger is often seen as a natural remedy for many health issues. But here’s the catch – too much of it can actually harm your body. Experts say moderation is the key. Let’s explore how much ginger per day is safe, its benefits, side effects, and the best ways to include it in your diet.
Health Benefits of Ginger
Ginger is loaded with antioxidants and natural compounds that support overall health. Some of the main benefits include;
- Boosts immunity and helps fight infections
- Improves digestion, reduces bloating, and relieves nausea
- Lowers inflammation and supports joint health
- May help balance blood sugar levels
- Relieves cold and cough symptoms naturally
How Much Ginger Per Day Is Safe
While ginger is healthy, consuming it in the right amount is important. Nutrition experts suggest:
- 2 to 4 grams of fresh ginger daily is safe for most adults
- Around 1 teaspoon of dry ginger powder is acceptable
- Children and older adults should consume even less
Eating more than this can irritate the stomach or interact with certain medication.
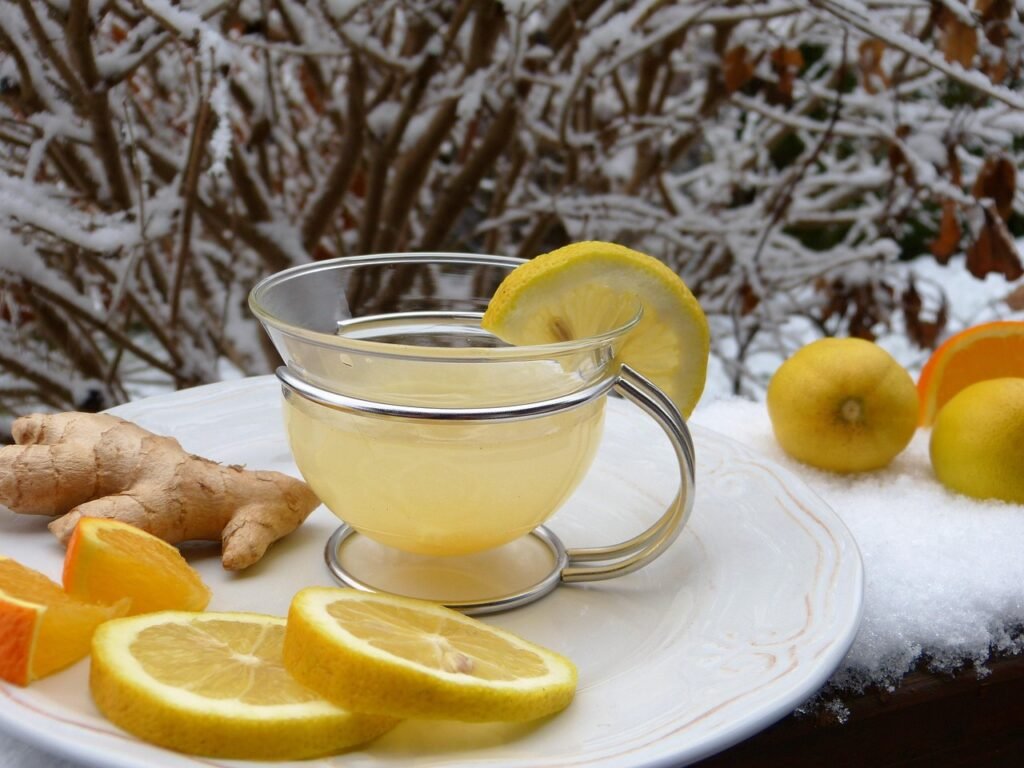

Side Effects of Too Much Ginger
Overconsumption of ginger may cause unexpected health issues. Some possible side effects include:
- Acidity and stomach irritation
- Heartburn or reflux
- Worsening of piles due to its heating nature
- Skin rashes or allergic reactions
- Hot flushes and scalp irritation
- Discomfort during menopause for sensitive individuals
Who Should Limit Ginger Intake
Certain groups need to be extra cautions with ginger. These include:
- Pregnant woman, as high amounts may trigger contractions
- People on blood-thinning medicines like aspirin or warfarin
- Those with ulcers, gallstones, or severe acidity
Consulting a doctor before regular use is advised if you have exciting health issues.
Safe Ways to Consume Ginger
The form and timing of ginger intake matter. Some safe options include:
- Ginger water made with fresh slices in warm water
- Ginger tea to relieve cold and bloating
- Adding grated ginger to curries, dals, and star-fries
- Using it in pickles and chutneys in small amounts
Morning consumption supports digestion, while ginger tea during cold or flu offers quick relief. However, avoid eating ginger late at night if you have acidity.
Fresh vs Dry Ginger
Both fresh and dry ginger are beneficial, but they have unique strengths:
- Fresh ginger is hydrating, rich in antioxidants, and ideal for colds
- Dry ginger powder is more concentrated and useful for specific remedies
Both forms add value to health, so choosing depends on your need.
Ginger is truly a superfood, but like every powerful ingredient, it works best in moderation. Around 2-4 grams a day is safe for most adults. Going beyond that may lead to side effects. The golden rule is balance – enjoy ginger in your teas, curries and remedies, but don’t overdo it.